The code we have for the calculator is robust but complicated. Let’s see what we can do to simplify it.
We’ll start with the obvious improvements.
A calculate function
We used this block of code twice to make calculations:
let newResultif (operator === 'plus') newResult = firstValue + secondValueif (operator === 'minus') newResult = firstValue - secondValueif (operator === 'times') newResult = firstValue * secondValueif (operator === 'divide') newResult = firstValue / secondValueLet’s put this into a function so it’s easier to understand. We’ll call it calculate.
function calculate() { // ...}First, we’ll copy-paste the entire code into calculate.
function calculate() { let newResult if (operator === 'plus') newResult = firstValue + secondValue if (operator === 'minus') newResult = firstValue - secondValue if (operator === 'times') newResult = firstValue * secondValue if (operator === 'divide') newResult = firstValue / secondValue}calculate needs to return the result, so we create a return statement.
function calculate() { let newResult if (operator === 'plus') newResult = firstValue + secondValue if (operator === 'minus') newResult = firstValue - secondValue if (operator === 'times') newResult = firstValue * secondValue if (operator === 'divide') newResult = firstValue / secondValue return newResult}But we don’t need the newResult variable in the function. We can use an early return pattern instead:
function calculate() { if (operator === 'plus') return firstValue + secondValue if (operator === 'minus') return firstValue - secondValue if (operator === 'times') return firstValue * secondValue if (operator === 'divide') return firstValue / secondValue}We know calculate needs three arguments:
firstValueoperatorsecondValue
Let’s put these arguments in.
function calculate(firstValue, operator, secondValue) { if (operator === 'plus') return firstValue + secondValue if (operator === 'minus') return firstValue - secondValue if (operator === 'times') return firstValue * secondValue if (operator === 'divide') return firstValue / secondValue}Here’s how we use calculate:
// In the operator sectionif ( previousButtonType !== 'operator' && previousButtonType !== 'equal' && typeof firstValue === 'number' && operator) { const newResult = calculate(firstValue, operator, secondValue) display.textContent = newResult calculator.dataset.firstValue = newResult} else { // ...}// In the equal sectionif (typeof firstValue === 'number' && operator) { const newResult = calculate(firstValue, operator, secondValue) display.textContent = newResult calculator.dataset.firstValue = newResult calculator.dataset.modifierValue = secondValue} else { // ...}Refresh and check your calculator. All tests should pass at this point.
Improving calculate
We need to make sure firstValue and secondValue are numbers before we perform a calculation. Right now, we do this before we use calculate. We do this in both the operator and equal sections.
if (buttonType === 'operator') { // ...
const firstValue = parseFloat(calculator.dataset.firstValue) const operator = calculator.dataset.operator const secondValue = parseFloat(result)
if (/*...*/) { // Calculate goes here }}if (buttonType === 'equal') { const firstValue = parseFloat(calculator.dataset.firstValue) const operator = calculator.dataset.operator const modifierValue = parseFloat(calculator.dataset.modifierValue) const secondValue = modifierValue || parseFloat(result)
if (/*...*/) { // Calculate goes here here }}If we use parsteFloat in calculate, we don’t have to use parseFloat in the operator and equal sections.
function calculate(firstValue, operator, secondValue) { firstValue = parseFloat(firstValue) secondValue = parseFloat(secondValue) if (operator === 'plus') return firstValue + secondValue if (operator === 'minus') return firstValue - secondValue if (operator === 'times') return firstValue * secondValue if (operator === 'divide') return firstValue / secondValue}Using the code:
if (buttonType === 'operator') { // ... // Removed need to parseFloat const firstValue = calculator.dataset.firstValue const operator = calculator.dataset.operator const secondValue = result
if ( previousButtonType !== 'operator' && previousButtonType !== 'equal' && // Removed need to check for numbers with `typeof` firstValue && operator ) { const newResult = calculate(firstValue, operator, secondValue) display.textContent = newResult calculator.dataset.firstValue = newResult } else { calculator.dataset.firstValue = result } // ...}if (buttonType === 'equal') { // Removed need to parseFloat const firstValue = calculator.dataset.firstValue const operator = calculator.dataset.operator const modifierValue = calculator.dataset.modifierValue const secondValue = modifierValue || result
// Removed need to check for numbers with `typeof` if (firstValue && operator) { const newResult = calculate(firstValue, operator, secondValue) display.textContent = newResult calculator.dataset.firstValue = newResult calculator.dataset.modifierValue = secondValue } else { display.textContent = parseFloat(result) * 1 }}Refresh and check your calculator again. All tests should still pass.
Reordering key handling
We handled keys in this order:
calculatorButtonsDiv.addEventListener('click', event => { // Number keys // Decimal key // Operator keys // Equal key // Clear key})I tried reading the code from top to bottom. When I did this, I realised I get overwhelmed when I reached the clear section. This is normal because the code for operators and equal are quite complicated.
Since we can handle keys in any order, I choose to bring the clear key up in the hierarchy. When I do this, code becomes easier to read. I know the hard parts will come at the bottom.
calculatorButtonsDiv.addEventListener('click', event => { // Clear key // Number keys // Decimal key // Operator keys // Equal key})Again, refresh the page and make sure all tests pass before you continue.
Refactoring Clear
Here’s what we wrote for the clear section.
if (buttonType === 'clear') { if (button.textContent === 'AC') { delete calculator.dataset.firstValue delete calculator.dataset.operator delete calculator.dataset.modifierValue }
display.textContent = '0' button.textContent = 'AC'}If you think the clear key looks hard to read, you’re not alone. The order of operations doesn’t make sense to my brain. It goes like this right now:
if (buttonType === 'clear') { // If clear key pressed twice, do this // If clear key pressed at least once, do that}It’ll make more sense if we flip things around.
if (buttonType === 'clear') { // If clear key pressed once, do this. // If clear key pressed twice, do that.}First, we’ll bring up the display.textContent and button.textContent lines.
if (buttonType === 'clear') { display.textContent = '0' button.textContent = 'AC' if (button.textContent === 'AC') { delete calculator.dataset.firstValue delete calculator.dataset.operator delete calculator.dataset.modifierValue }}We cannot check for the button’s textContent to reset the calculator anymore. We can, however, check if the user pressed the clear key previously.
if (buttonType === 'clear') { display.textContent = '0' button.textContent = 'AC' if (previousButtonType === 'clear') { delete calculator.dataset.firstValue delete calculator.dataset.operator delete calculator.dataset.modifierValue }}This is much simpler compared to before!
Changing variable names
We use the variable result to signify the displayed value from the calculator.
const result = display.textContentThis can make things confusing because result usually signifies the result (after processing). We should use variable name like displayValue instead. displayValue is better because it describes the value it stores.
Let’s change all instances of result into displayValue. If you use Visual Studio Code, you can change all affected instances of a variable by pressing f2.

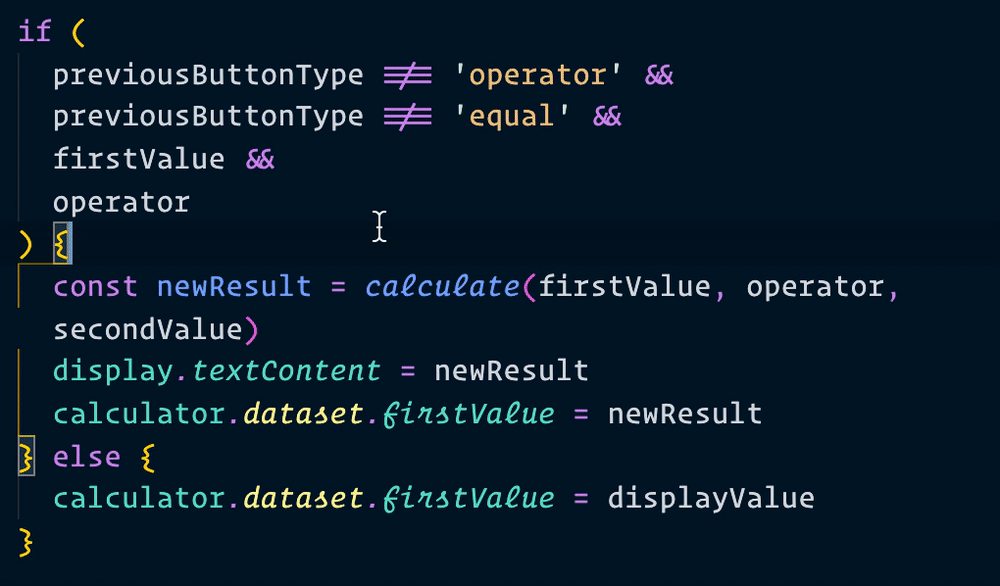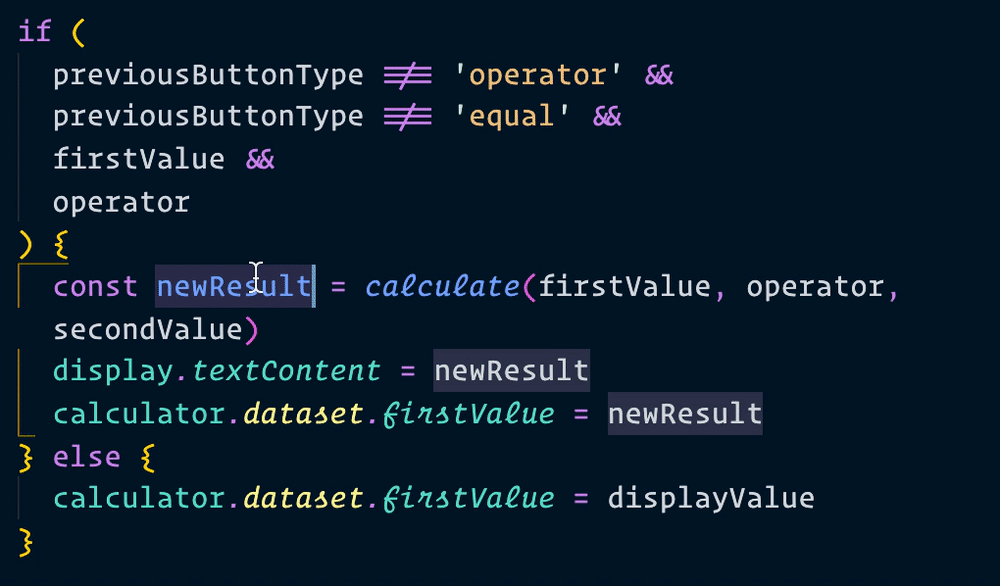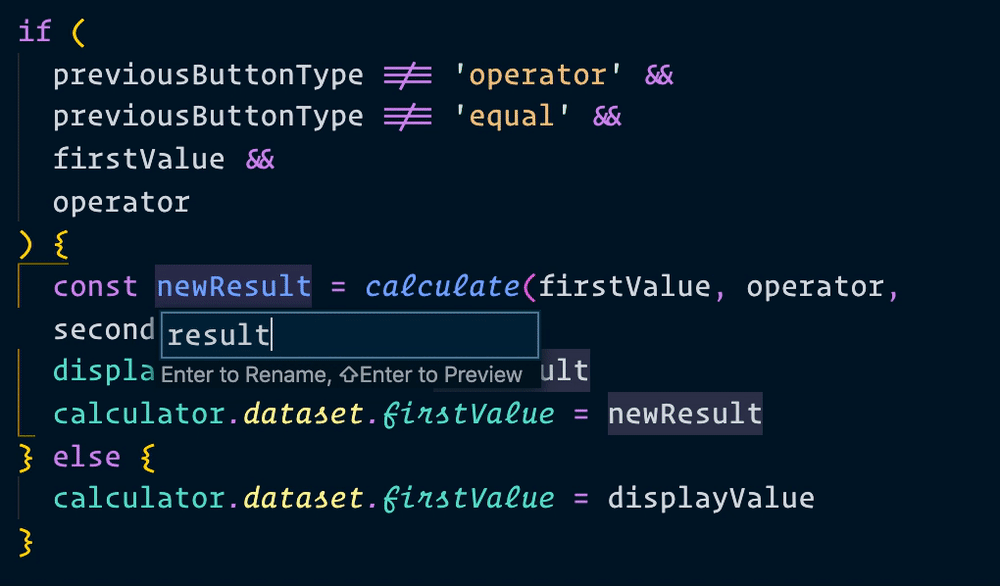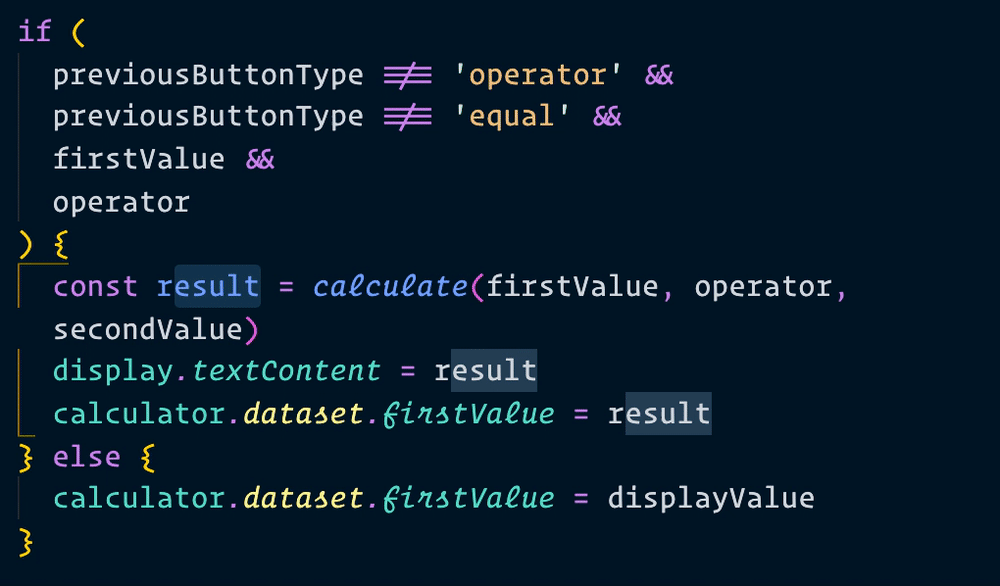
Now, when we make a calculation, we can use result instead of newResult. We’ll change all instances of newResult to result as well.
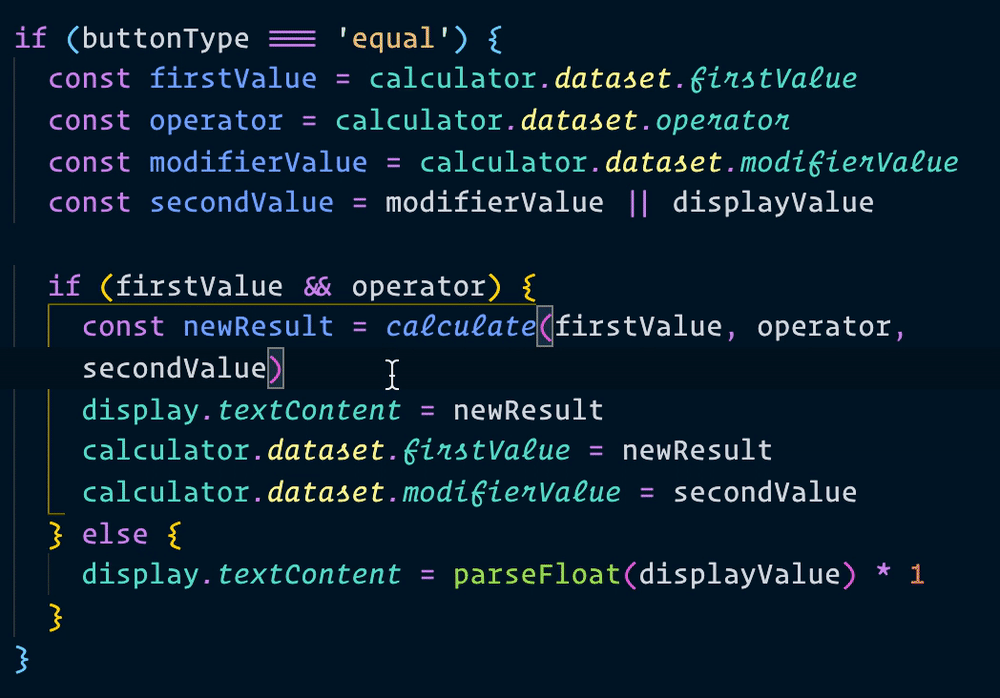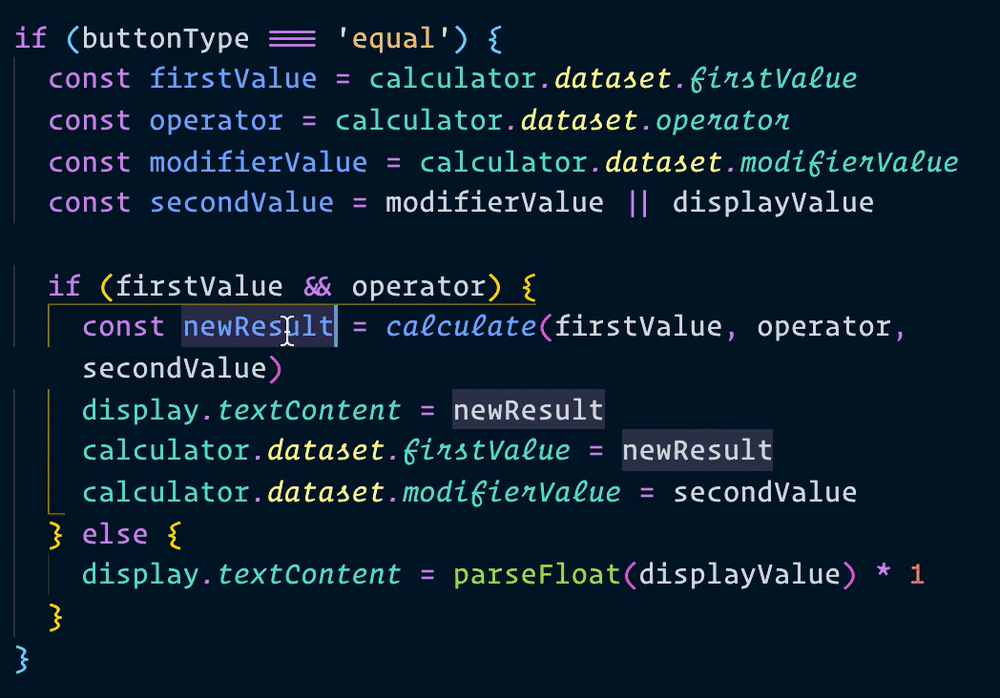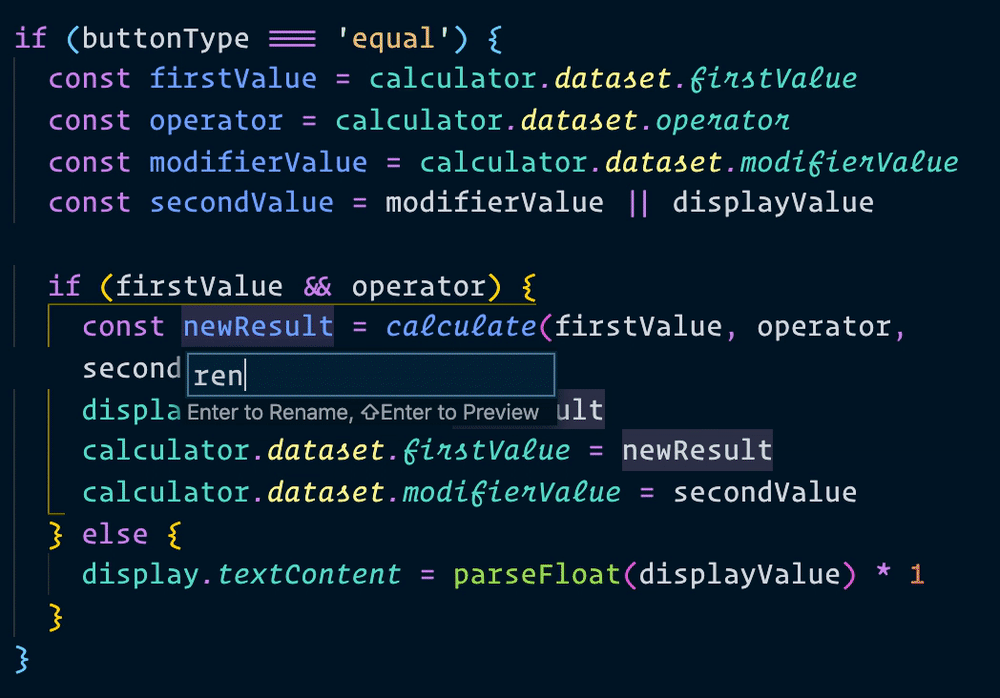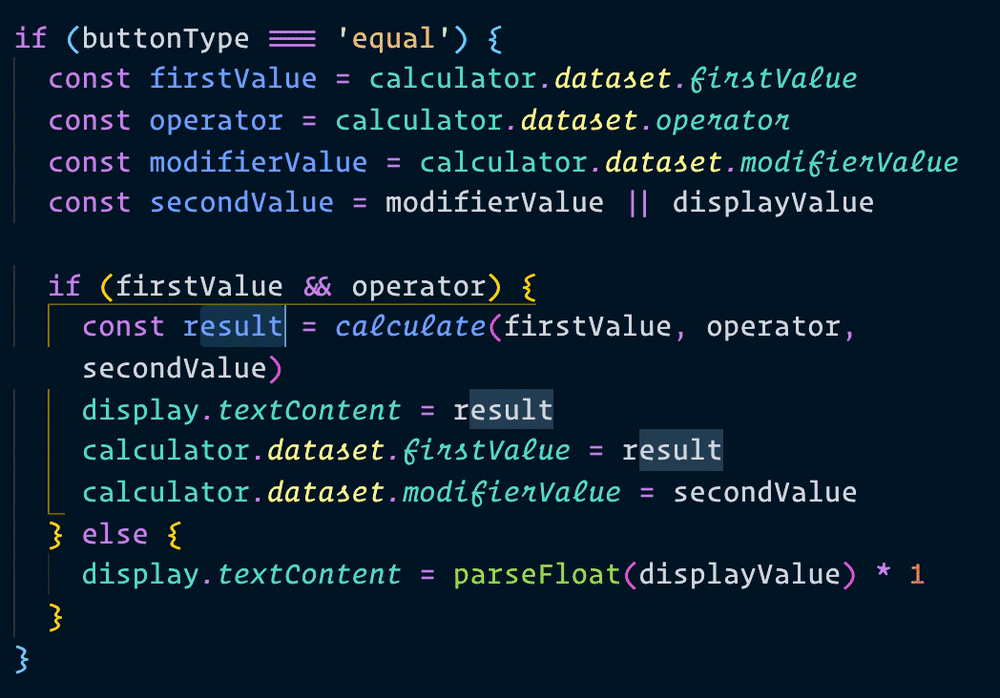
That’s it!
There’s is one more thing I’d like to refactor. But before that, we need to introduce the switch statement.
Welcome! Unfortunately, you don’t have access to this lesson. To get access, please purchase the course or enroll in Magical Dev School.
Unlock this lesson